Proximity switch (sensor)
What is a proximity switch (sensor)?
A proximity switch is a switch that detects the proximity or absence of an object without making contact with the object to be detected. The JIS standard defines proximity switches as "position sensing switches that operate without mechanical contact by a moving part. (Standard: JIS C 8201-5-2 (Corresponding international standard: IEC 60947-5-2/IDT a))
Proximity switches are classified into the following four categories according to the method of operation.
Proximity switches are classified into the following four categories according to the method of operation.
Inductive and capacitive proximity switches
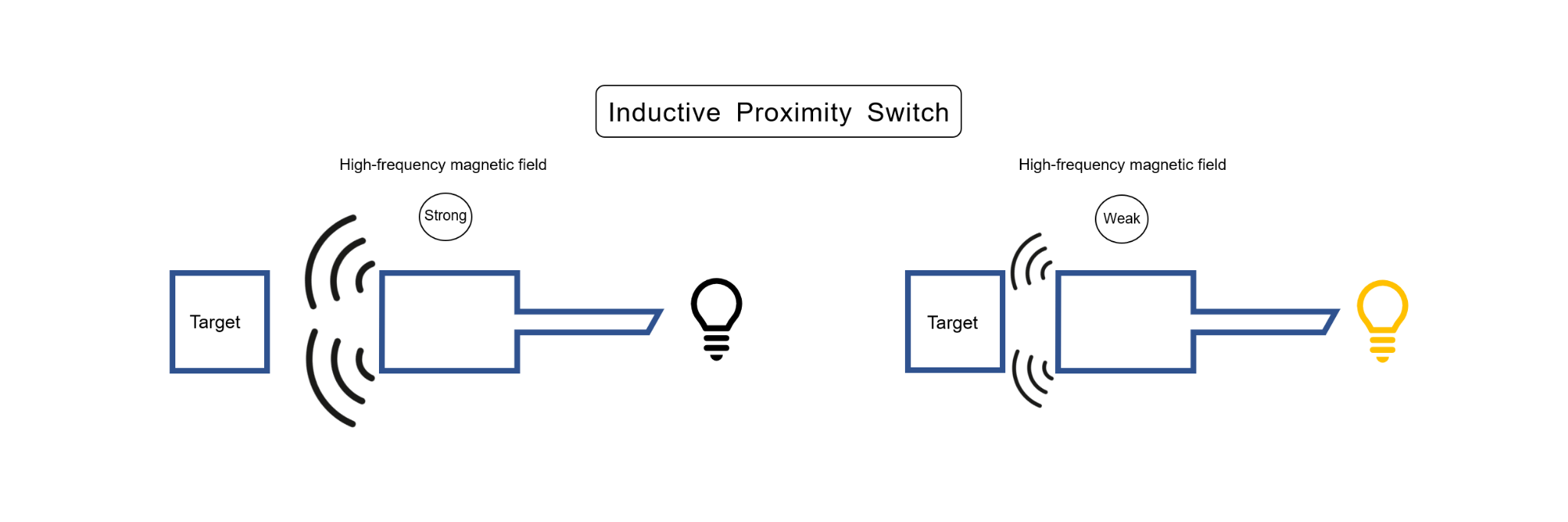
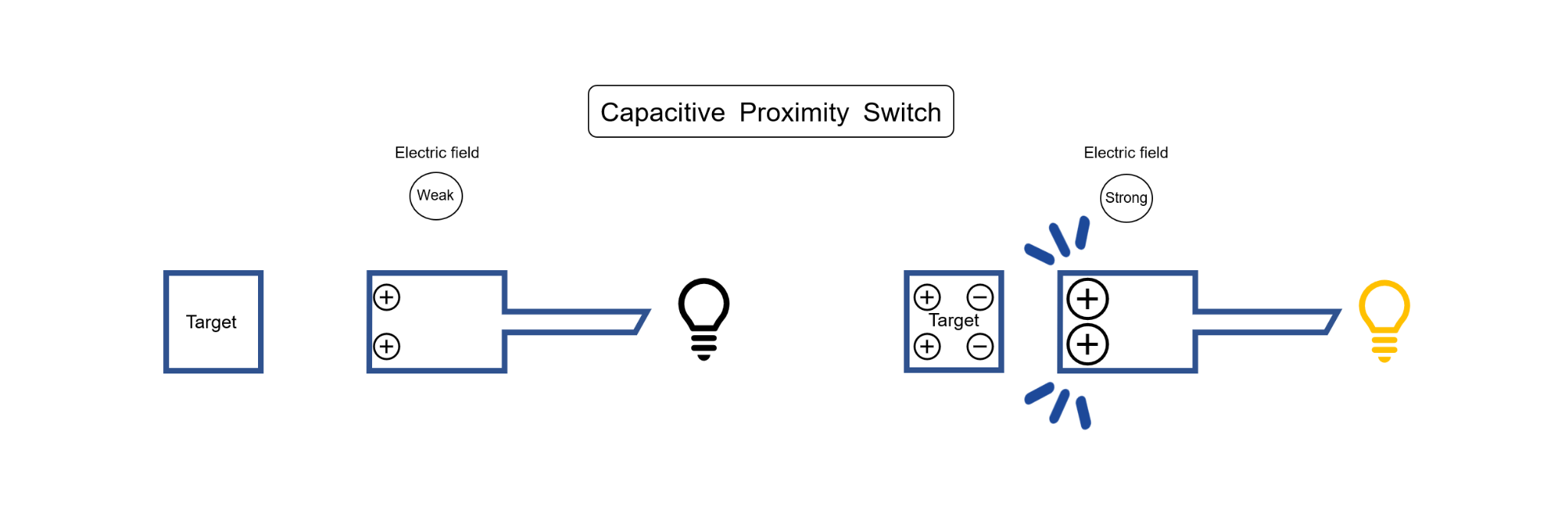
Defined in the JIS standard as "a switch that determines the output signal by the presence or absence of a sensing element that absorbs or changes the energy emitted from the sensing surface in an electromagnetic or electric field." The inductive proximity switch detects the presence of metallic and/or non-metallic objects. Inductive proximity switches detect the attenuation of high-frequency magnetic fields, while capacitive proximity switches detect the amplification of electric fields.
Defined in the JIS standard as "a switch that determines the output signal by the presence or absence of a sensing element that absorbs or changes the energy emitted from the sensing surface in an electromagnetic or electric field." The inductive proximity switch detects the presence of metallic and/or non-metallic objects. Inductive proximity switches detect the attenuation of high-frequency magnetic fields, while capacitive proximity switches detect the amplification of electric fields.
Ultrasonic proximity switch
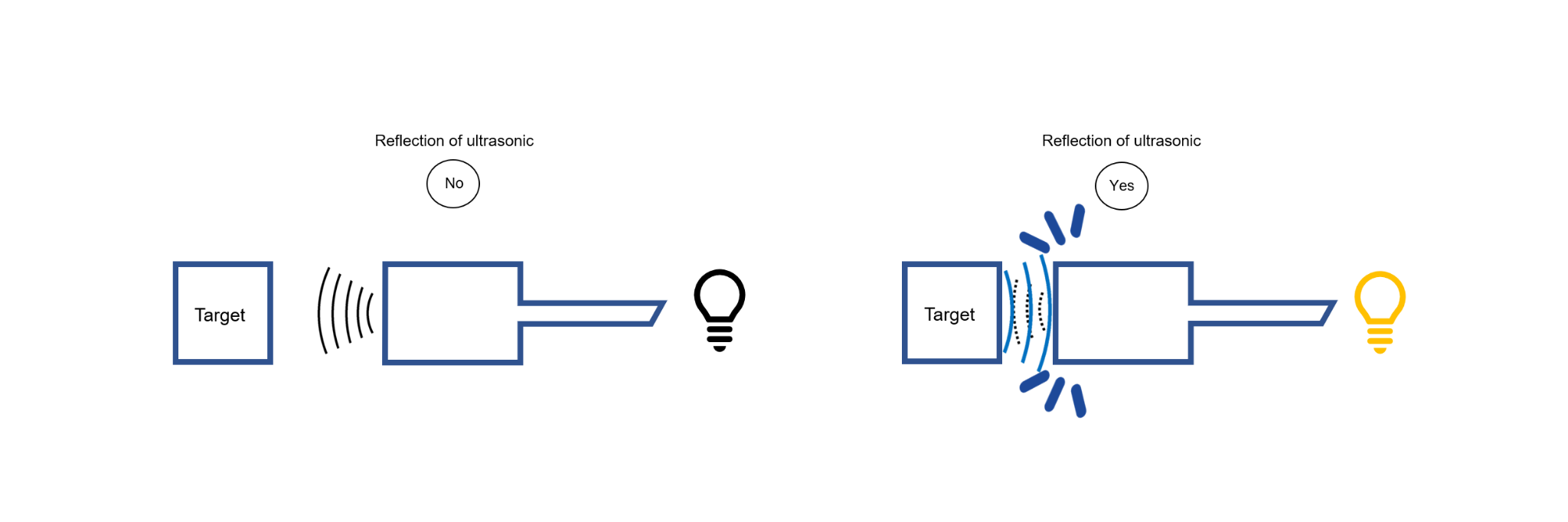
The JIS standard defines an ultrasonic proximity switch as "an ultrasonic proximity switch whose output signal is determined by the presence or absence of a sensing object that reflects ultrasonic energy emitted from the sensing surface within the sensing area." The presence of an acoustic reflecting object is detected. The transmitter and receiver are either integrated or separated. Some have a reflector and detect the time difference between the transmitted and reflected waves when intercepted by a detecting object.
The JIS standard defines an ultrasonic proximity switch as "an ultrasonic proximity switch whose output signal is determined by the presence or absence of a sensing object that reflects ultrasonic energy emitted from the sensing surface within the sensing area." The presence of an acoustic reflecting object is detected. The transmitter and receiver are either integrated or separated. Some have a reflector and detect the time difference between the transmitted and reflected waves when intercepted by a detecting object.
Photoelectric proximity switches
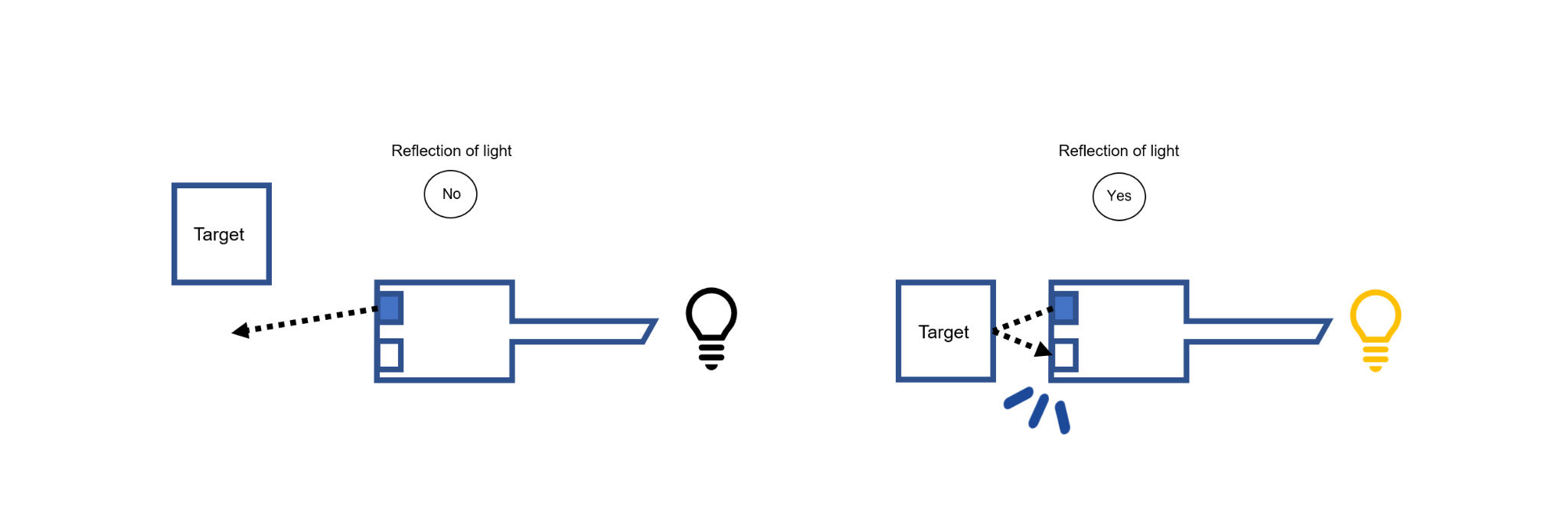
The JIS standard defines a photoelectric proximity switch as "a switch whose output signal is determined by the presence or absence of a detecting body that reflects or blocks visible or invisible light emitted from a light projector. The presence of an object blocking the light beam is detected. The light emitter and receiver are either integrated or separated.
The JIS standard defines a photoelectric proximity switch as "a switch whose output signal is determined by the presence or absence of a detecting body that reflects or blocks visible or invisible light emitted from a light projector. The presence of an object blocking the light beam is detected. The light emitter and receiver are either integrated or separated.
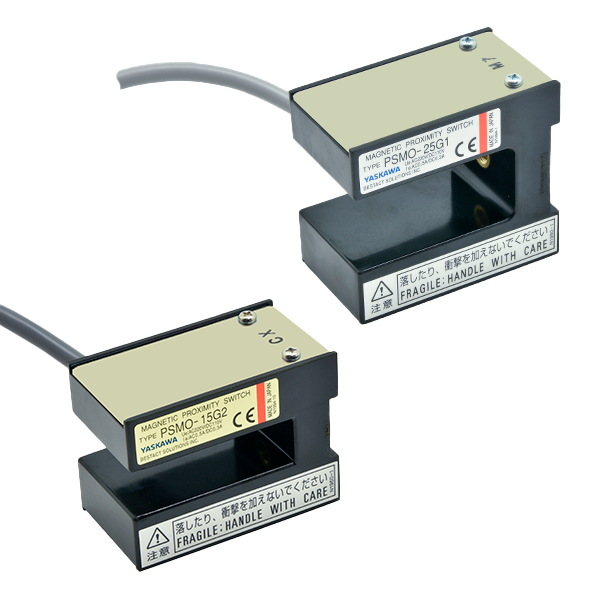
Magnetic proximity switches
The JIS standard defines a magnetic proximity switch as "a switch whose output signal is determined by the presence or absence of an object that causes a change in the magnetic field within the detection area. The magnetic proximity switch detects the presence of an object by means of a magnetic field.
The following is a detailed explanation of magnetic proximity switches.
The JIS standard defines a magnetic proximity switch as "a switch whose output signal is determined by the presence or absence of an object that causes a change in the magnetic field within the detection area. The magnetic proximity switch detects the presence of an object by means of a magnetic field.
The following is a detailed explanation of magnetic proximity switches.

Definition of magnetic proximity switch (sensor)
A magnetic proximity switch outputs a signal depending on the presence or absence of an object that causes a change in the magnetic field within the detection area without contacting the object. The built-in sensing element can be a reed switch with a mechanical contact point, a Hall element using the Hall effect, or a magnetoresistive element whose electrical resistance value fluctuates. Yaskawa Power Reed Switches (BESTACT), which have a unique structure, are used as the sensing element in the magnetic proximity switches we manufacture.
Operating principle of magnetic proximity switches (sensors)
When a magnet approaches the switch, the reed switch inside the switch reacts to the magnetism. As shown in the figure below, when the magnet is close to the switch, the contacts operate. Conversely, when the magnet is separated from the switch, the magnetism applied to the switch is weakened and the contacts are restored.

The switch has two types: a-contact (normally open type / NO type) and b-contact (normally closed type / NC type). a-contact is normally OFF and is switched to ON by the approach of a detector (change in magnetic field). Contact b is normally ON and changes to OFF when the detector approaches (change in magnetic field). The state of energization and disconnection of the contact is the reverse of the above figure.
Types and Usage of Magnetic Proximity Switches (Sensors)
Magnetic proximity switches can be broadly classified into two types: those in which the switch and magnet are integrated, as typified by the vane type, and those in which they are separated.
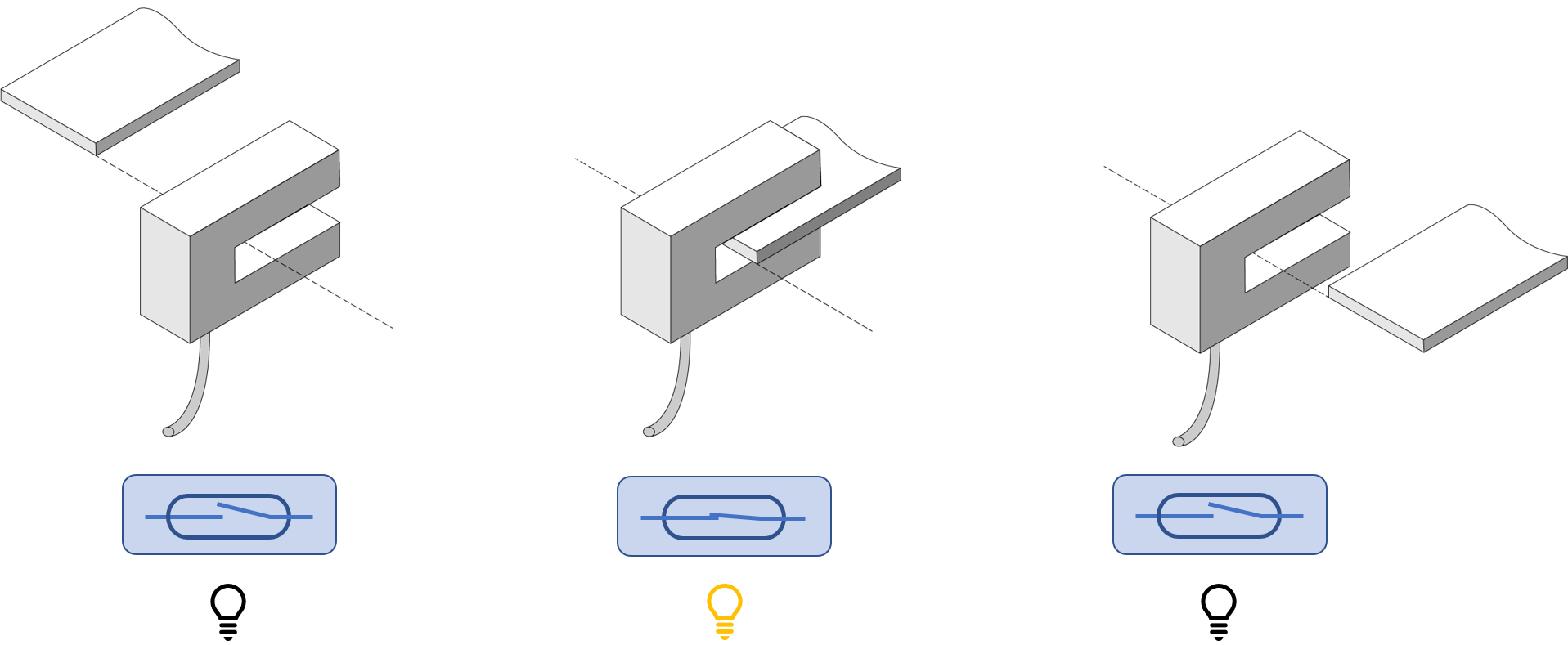
The vane type has the switch and magnet in one piece.
Switching occurs when a flat plate-shaped sensing element (ferromagnetic material: iron plate, etc.) passes through the U-shaped groove. The detection is made by shielding the magnetic path formed by the intrusion of the detecting body between the magnet and the reed switch, which are arranged in the form of a groove. As mentioned above, when the switch is a b-contact, the following reed switch energized/disconnected states caused by the proximity of the sensing body are reversed.
The vane type has the switch and magnet in one piece.
Switching occurs when a flat plate-shaped sensing element (ferromagnetic material: iron plate, etc.) passes through the U-shaped groove. The detection is made by shielding the magnetic path formed by the intrusion of the detecting body between the magnet and the reed switch, which are arranged in the form of a groove. As mentioned above, when the switch is a b-contact, the following reed switch energized/disconnected states caused by the proximity of the sensing body are reversed.
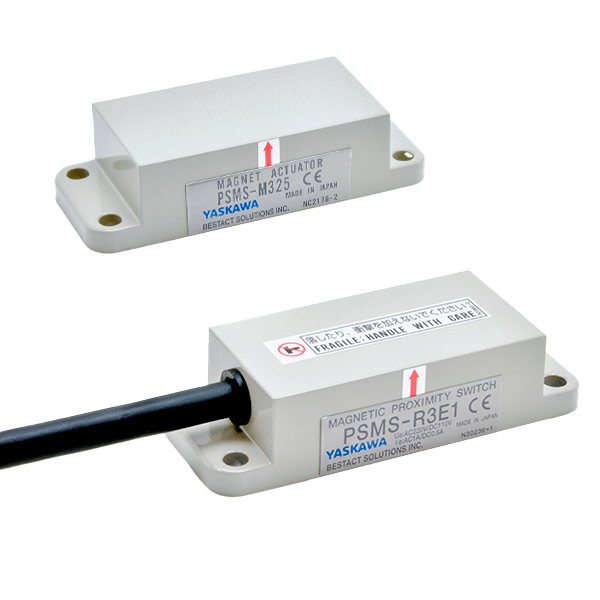
Separate switch and magnet type (separate type, cylindrical type, memory type)
The switch is fixed and the magnet is attached to the moving object. Switching occurs when the magnet approaches or passes through the switch. There are also separate type switches and magnets as shown in the figure below, cylindrical type switches, and memory type switches that retain the ON state after the magnet passes through. The operating principle is the same, but the direction in which the magnet passes through is specified by each product. As mentioned above, when the switch is a b-contact, the following reed switch energized/disconnected states caused by the proximity of the sensing object are reversed.

How to Select Magnetic Proximity Switches (Sensors)
The main performance factors to check when selecting a magnetic proximity switch suitable for the installation environment are the sensing distance, electrical specifications, and applicable ambient temperature.
The sensing distance refers to the distance between the sensing surface of the switch and any surface of the magnet. Since the size of the magnet is related to the strength of the magnetism, it is necessary to select a set of switch and magnet that satisfies the detection distance (impressed distance). In addition, there is hysteresis, which is the difference between the operating point and the return point of the switch. Therefore, it is necessary to check the detection distance expressed in the operating characteristics of the product specifications.
The electrical specifications depend on the performance of the built-in contacts. Select a switch after confirming the rated operating current.
Here we introduce the contact performance of the aforementioned Yaskawa power reed switch (BESTACT).
The ambient temperature is the temperature range in which the switch can be operated without any problem. It depends on the temperature range of the resin used to fill the switch and magnet, and the temperature range of the case that covers the switch and magnet. The high-temperature switches we handle can operate up to 130°C.
The sensing distance refers to the distance between the sensing surface of the switch and any surface of the magnet. Since the size of the magnet is related to the strength of the magnetism, it is necessary to select a set of switch and magnet that satisfies the detection distance (impressed distance). In addition, there is hysteresis, which is the difference between the operating point and the return point of the switch. Therefore, it is necessary to check the detection distance expressed in the operating characteristics of the product specifications.
The electrical specifications depend on the performance of the built-in contacts. Select a switch after confirming the rated operating current.
Here we introduce the contact performance of the aforementioned Yaskawa power reed switch (BESTACT).
| Bestact type | R25 | R15 | remarks | |
| Rated operating current | AC | 220V 0.5A | 220V 1A | induced load(50/60Hz) |
| DC | 110V 0.3A | 110V 0.5A , 220V 0.2A | induced load(R25:L/R=40ms R15:L/R=100ms) | |
The ambient temperature is the temperature range in which the switch can be operated without any problem. It depends on the temperature range of the resin used to fill the switch and magnet, and the temperature range of the case that covers the switch and magnet. The high-temperature switches we handle can operate up to 130°C.
Yaskawa Power Reed Switches (BESTACT) are used for the sensing part of the magnetic proximity switches we handle, which are long-lasting and highly reliable. Please try our magnetic proximity switches with built-in BESTACT, which have been selected for more than 40 years.






